User Codes
Astrophysics
Athena (explicit, uniform grid MHD code)
Athena is a straightforward C code which doesn't use a lot of libraries so it is pretty straightforward to build and compile on new machines.
It encapsulates its compiler flags, etc in an Makeoptions.in file which is then processed by configure. I've used the following additions to Makeoptions.in on TCS and GPC:
<source lang="sh"> ifeq ($(MACHINE),scinettcs)
CC = mpcc_r LDR = mpcc_r OPT = -O5 -q64 -qarch=pwr6 -qtune=pwr6 -qcache=auto -qlargepage -qstrict MPIINC = MPILIB = CFLAGS = $(OPT) LIB = -ldl -lm
else ifeq ($(MACHINE),scinetgpc)
CC = mpicc LDR = mpicc OPT = -O3 MPIINC = MPILIB = CFLAGS = $(OPT) LIB = -lm
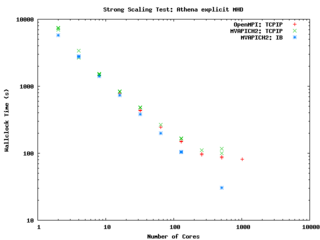
else ... endif endif </source> It performs quite well on the GPC, scaling extremely well even on a strong scaling test out to about 256 cores (32 nodes) on Gigabit ethernet, and performing beautifully on InfiniBand out to 512 cores (64 nodes).
-- ljdursi 19:20, 13 August 2009 (UTC)
FLASH3 (Adaptive Mesh reactive hydrodynamics; explict hydro/MHD)
FLASH encapsulates its machine-dependant information in the FLASH3/sites directory. For the GPC, you'll have to
module load intel module load openmpi module load hdf5/183-v16-openmpi
and with that, the following file (sites/scinetgpc/Makefile.h) works for me: <source lang="sh">
- Must do module load hdf5/183-v16-openmpi
HDF5_PATH = ${SCINET_HDF5_BASE} ZLIB_PATH = /usr/local
- ----------------------------------------------------------------------------
- Compiler and linker commands
- We use the f90 compiler as the linker, so some C libraries may explicitly
- need to be added into the link line.
- ----------------------------------------------------------------------------
- modules will put the right mpi in our path
FCOMP = mpif77 CCOMP = mpicc CPPCOMP = mpiCC LINK = mpif77
- ----------------------------------------------------------------------------
- Compilation flags
- Three sets of compilation/linking flags are defined: one for optimized
- code, one for testing, and one for debugging. The default is to use the
- _OPT version. Specifying -debug to setup will pick the _DEBUG version,
- these should enable bounds checking. Specifying -test is used for
- flash_test, and is set for quick code generation, and (sometimes)
- profiling. The Makefile generated by setup will assign the generic token
- (ex. FFLAGS) to the proper set of flags (ex. FFLAGS_OPT).
- ----------------------------------------------------------------------------
FFLAGS_OPT = -c -r8 -i4 -O3 -xSSE4.2 FFLAGS_DEBUG = -c -g -r8 -i4 -O0 FFLAGS_TEST = -c -r8 -i4
- if we are using HDF5, we need to specify the path to the include files
CFLAGS_HDF5 = -I${HDF5_PATH}/include
CFLAGS_OPT = -c -O3 -xSSE4.2 CFLAGS_TEST = -c -O2 CFLAGS_DEBUG = -c -g
MDEFS =
.SUFFIXES: .o .c .f .F .h .fh .F90 .f90
- ----------------------------------------------------------------------------
- Linker flags
- There is a seperate version of the linker flags for each of the _OPT,
- _DEBUG, and _TEST cases.
- ----------------------------------------------------------------------------
LFLAGS_OPT = -o LFLAGS_TEST = -o LFLAGS_DEBUG = -g -o
MACHOBJ =
MV = mv -f
AR = ar -r
RM = rm -f
CD = cd
RL = ranlib
ECHO = echo
</source>
-- ljdursi 22:11, 13 August 2009 (UTC)
Aeronautics
Chemistry
GAMESS (US)
Please refer to the GAMESS (US) page.
User supplied content below.
Tips from the Fekl Lab
Through trial and error, we have found a few useful things that we would like to share:
1. Two very useful, open-source programs for visualization of output files from GAMESS(US) and for generation of input files are MacMolPltand Avogadro. The are available for UNIX/LINUX, Windows and Mac based machines, HOWEVER: any input files that we have generated with these programs on a Windows-based machine do not run on Mac based machines. We don't know why.
2. WinSCP is a very useful tool that has a graphical user interface for moving files from a local machine to SCINET and vice versa. It also has text editing capabilities.
3. The ESML Basis Set Exchange is an excellent source for custom basis set or effective core potential parameters. Make sure that you specify "Gamess-US" in the format drop-down box.
4. The commercial program ChemCraft is a highly useful visualization program that has the ability to edit molecules in a very similar fashion to GaussView. It can also be customized to build GAMESS(US) input files.
Anatomy of a GAMESS(US) Input File with Basis Set Info in an External File
$CONTRL SCFTYP=RHF RUNTYP=OPTIMIZE DFTTYP=M06-L MAXIT=199 MULT=1 NOSYM=1
ECP=READ $END
$SYSTEM TIMLIM=525600 MWORDS=1750 PARALL=.TRUE. $END
$BASIS GBASIS=CUSTOMNI EXTFIL=.t. $END
$SCF DIRSCF=.TRUE. FDIFF=.f. $END
$STATPT OPTTOL=0.0001 NSTEP=500 HSSEND=.t. $END
$DATA
Mo_BDT3
C1
MOLYBDENUM 42.0 5.7556500000 4.4039600000 16.5808400000
SULFUR 16.0 7.4169700000 3.1956300000 15.2089300000
SULFUR 16.0 4.0966800000 3.2258300000 15.1761100000
SULFUR 16.0 3.9677300000 4.4940500000 18.3266100000
SULFUR 16.0 7.1776900000 3.5815000000 18.4485200000
SULFUR 16.0 4.3776600000 6.2447400000 15.6786900000
SULFUR 16.0 7.5478700000 6.0679800000 16.2223700000
CARBON 6.0 6.4716900000 2.1004800000 14.1902300000
CARBON 6.0 5.0690300000 2.1781400000 14.1080700000
CARBON 6.0 4.8421800000 4.2701300000 19.8855500000
CARBON 6.0 6.1969000000 3.9249600000 19.9397400000
CARBON 6.0 6.8280600000 3.7834200000 21.1913200000
CARBON 6.0 5.7697600000 7.6933500000 17.4241800000
CARBON 6.0 7.2043100000 7.9413600000 17.8281100000
CARBON 6.0 5.5051400000 7.0409700000 14.5903800000
CARBON 6.0 6.8905200000 6.9194700000 14.7626200000
CARBON 6.0 7.7396400000 7.5379800000 13.8285700000
HYDROGEN 1.0 8.8190700000 7.4520600000 13.9252200000
CARBON 6.0 7.2169400000 8.2960300000 12.7704100000
HYDROGEN 1.0 7.8667000000 8.7825100000 12.0575600000
CARBON 6.0 5.8260300000 8.4502300000 12.6467800000
HYDROGEN 1.0 5.4143000000 9.0544300000 11.8493100000
CARBON 6.0 4.9881500000 7.8192300000 13.5528400000
HYDROGEN 1.0 3.9090500000 7.9420000000 13.4583700000
CARBON 6.0 7.1538500000 1.1569600000 13.4143900000
CARBON 6.0 4.4018100000 1.3603900000 13.1919900000
CARBON 6.0 6.4791600000 0.3185500000 12.5353300000
CARBON 6.0 5.0837400000 0.4369500000 12.4084900000
HYDROGEN 1.0 7.0116000000 -0.4099400000 11.9434600000
HYDROGEN 1.0 8.2399000000 1.0702400000 13.4937600000
HYDROGEN 1.0 3.3185600000 1.4368700000 13.0953100000
HYDROGEN 1.0 4.5549800000 -0.1997300000 11.7165200000
CARBON 6.0 6.1105700000 3.9639000000 22.3866100000
CARBON 6.0 4.1216300000 4.4424400000 21.1020100000
HYDROGEN 1.0 7.8732900000 3.5217100000 21.2520500000
CARBON 6.0 4.7606000000 4.2868500000 22.3363800000
HYDROGEN 1.0 6.6064200000 3.8406000000 23.3428500000
HYDROGEN 1.0 4.2065000000 4.4170700000 23.2667100000
HYDROGEN 1.0 3.0674000000 4.6893500000 21.0889000000
HYDROGEN 1.0 7.4249200000 7.7545300000 18.8583200000
HYDROGEN 1.0 7.6651700000 8.9049700000 17.7652100000
HYDROGEN 1.0 5.3324000000 8.6487800000 17.2222700000
HYDROGEN 1.0 5.5015000000 7.1039000000 18.2759400000
$END
$ECP
MO-ECP GEN 28 3
5 ----- f potential -----
-0.0469492 0 537.9667807
-20.2080084 1 147.8982938
-106.2116302 2 45.7358898
-41.8107368 2 13.2911467
-4.2054103 2 4.7059961
3 ----- s-f potential -----
2.8063717 0 110.2991760
44.5162012 1 23.2014645
82.7785227 2 5.3530131
4 ----- p-f potential -----
4.9420876 0 63.2901397
25.8604976 1 23.3315302
132.4708742 2 24.6759423
57.3149794 2 4.6493040
5 ----- d-f potential -----
3.0054591 0 104.4839977
26.3637851 1 66.2307245
183.3849199 2 39.1283176
98.4453068 2 13.1164437
22.4901377 2 3.6280263
S NONE
S NONE
S NONE
S NONE
S NONE
S NONE
C NONE
C NONE
C NONE
C NONE
C NONE
C NONE
C NONE
C NONE
C NONE
C NONE
H NONE
C NONE
H NONE
C NONE
H NONE
C NONE
H NONE
C NONE
C NONE
C NONE
C NONE
H NONE
H NONE
H NONE
H NONE
C NONE
C NONE
H NONE
C NONE
H NONE
H NONE
H NONE
H NONE
H NONE
H NONE
H NONE
$END
The Input Deck
Below is the input deck. It is where you tell GAMESS(US) what job type to execute and where all you individual parameters are entered for your specific job type. The example input deck below is for a geometry optimization and frequency calculation. This input deck is equivalent to the Gaussian job with "opt" and "freq" in the route section.
$CONTRL SCFTYP=RHF RUNTYP=OPTIMIZE DFTTYP=M06-L MAXIT=199 MULT=1 NOSYM=1 ECP=READ $END $SYSTEM TIMLIM=2850 MWORDS=1750 MEMDDI=20 PARALL=.TRUE. $END $BASIS GBASIS=CUSTOMNI EXTFIL=.t. $END $SCF DIRSCF=.TRUE. FDIFF=.f. $END $STATPT OPTTOL=0.0001 NSTEP=500 HSSEND=.t. $END $DATA
An important thing to note is the spacing. In the input deck, there must be 1 space at the beginning of each line of the input deck. If not, the job will fail. Most builders will insert this space anyway, but it helps to double check.
The end of the input deck is marked by the "$DATA" line.
Job Title Line
The next line of the file is the job title. It can be anthing you wish, however, we have found that to be on the safe side, we avoide using symbols or spaces
Mo_BDT3
Symmetry Point Group
The next line of the file is the symmetry point group of your molecule. Note that there is no leading space before the point group.
C1
Coordinates
The next block of text is set aside for the coordinates of the molecule. This can be in internal (or z-matrix) format or cartesian coordinates. Note that there is no leading space before the coordinates. One may use the chemical symbol or the full name of each atom in the molecule. Note that the end of the coordinates is signified by an "$END", which MUST have one space preceding it. The coordinates below do NOT have any basis set information inserted. It is possible to insert basis set information directly into the input file. This is accomplished by obtaining the desired basis set parameters from the EMSL and then inserting them below each relevant atom. An example input file with inserted basis set information will be shown later.
MOLYBDENUM 42.0 5.7556500000 4.4039600000 16.5808400000 SULFUR 16.0 7.4169700000 3.1956300000 15.2089300000 SULFUR 16.0 4.0966800000 3.2258300000 15.1761100000 SULFUR 16.0 3.9677300000 4.4940500000 18.3266100000 SULFUR 16.0 7.1776900000 3.5815000000 18.4485200000 SULFUR 16.0 4.3776600000 6.2447400000 15.6786900000 SULFUR 16.0 7.5478700000 6.0679800000 16.2223700000 CARBON 6.0 6.4716900000 2.1004800000 14.1902300000 CARBON 6.0 5.0690300000 2.1781400000 14.1080700000 CARBON 6.0 4.8421800000 4.2701300000 19.8855500000 CARBON 6.0 6.1969000000 3.9249600000 19.9397400000 CARBON 6.0 6.8280600000 3.7834200000 21.1913200000 CARBON 6.0 5.7697600000 7.6933500000 17.4241800000 CARBON 6.0 7.2043100000 7.9413600000 17.8281100000 CARBON 6.0 5.5051400000 7.0409700000 14.5903800000 CARBON 6.0 6.8905200000 6.9194700000 14.7626200000 CARBON 6.0 7.7396400000 7.5379800000 13.8285700000 HYDROGEN 1.0 8.8190700000 7.4520600000 13.9252200000 CARBON 6.0 7.2169400000 8.2960300000 12.7704100000 HYDROGEN 1.0 7.8667000000 8.7825100000 12.0575600000 CARBON 6.0 5.8260300000 8.4502300000 12.6467800000 HYDROGEN 1.0 5.4143000000 9.0544300000 11.8493100000 CARBON 6.0 4.9881500000 7.8192300000 13.5528400000 HYDROGEN 1.0 3.9090500000 7.9420000000 13.4583700000 CARBON 6.0 7.1538500000 1.1569600000 13.4143900000 CARBON 6.0 4.4018100000 1.3603900000 13.1919900000 CARBON 6.0 6.4791600000 0.3185500000 12.5353300000 CARBON 6.0 5.0837400000 0.4369500000 12.4084900000 HYDROGEN 1.0 7.0116000000 -0.4099400000 11.9434600000 HYDROGEN 1.0 8.2399000000 1.0702400000 13.4937600000 HYDROGEN 1.0 3.3185600000 1.4368700000 13.0953100000 HYDROGEN 1.0 4.5549800000 -0.1997300000 11.7165200000 CARBON 6.0 6.1105700000 3.9639000000 22.3866100000 CARBON 6.0 4.1216300000 4.4424400000 21.1020100000 HYDROGEN 1.0 7.8732900000 3.5217100000 21.2520500000 CARBON 6.0 4.7606000000 4.2868500000 22.3363800000 HYDROGEN 1.0 6.6064200000 3.8406000000 23.3428500000 HYDROGEN 1.0 4.2065000000 4.4170700000 23.2667100000 HYDROGEN 1.0 3.0674000000 4.6893500000 21.0889000000 HYDROGEN 1.0 7.4249200000 7.7545300000 18.8583200000 HYDROGEN 1.0 7.6651700000 8.9049700000 17.7652100000 HYDROGEN 1.0 5.3324000000 8.6487800000 17.2222700000 HYDROGEN 1.0 5.5015000000 7.1039000000 18.2759400000 $END
Effective Core Potential Data
The effective core potential (ECP) data is entered after the coordinates. It starts with "$ECP", which must be preceded with a space. The atoms of the molecule are listed in the same order as in the coordinates section and the parameters for the ECP are listed after each atom. Note that for any atom that does NOT have an ECP, one must enter "ECP-NONE" or "NONE" after each atom without an ECP.
$ECP
MO-ECP GEN 28 3
5 ----- f potential -----
-0.0469492 0 537.9667807
-20.2080084 1 147.8982938
-106.2116302 2 45.7358898
-41.8107368 2 13.2911467
-4.2054103 2 4.7059961
3 ----- s-f potential -----
2.8063717 0 110.2991760
44.5162012 1 23.2014645
82.7785227 2 5.3530131
4 ----- p-f potential -----
4.9420876 0 63.2901397
25.8604976 1 23.3315302
132.4708742 2 24.6759423
57.3149794 2 4.6493040
5 ----- d-f potential -----
3.0054591 0 104.4839977
26.3637851 1 66.2307245
183.3849199 2 39.1283176
98.4453068 2 13.1164437
22.4901377 2 3.6280263
S NONE
S NONE
S NONE
S NONE
S NONE
S NONE
C NONE
C NONE
C NONE
C NONE
C NONE
C NONE
C NONE
C NONE
C NONE
C NONE
H NONE
C NONE
H NONE
C NONE
H NONE
C NONE
H NONE
C NONE
C NONE
C NONE
C NONE
H NONE
H NONE
H NONE
H NONE
C NONE
C NONE
H NONE
C NONE
H NONE
H NONE
H NONE
H NONE
H NONE
H NONE
H NONE
$END
-- mzd 16 November 2009
Using Effective Core Potentials in GAMESS(US)
For many metal containing compounds, it is very convenient and time saving to use an effective core potential (ECP) for the core metal electrons, as they are usually not important to the reactivity of the complex or the geometry around the metal. Since GAMESS(US) has a limited number of built-in ECPs, one may want to make GAMESS(US) read an external file that contains the ECP data using the "EXTFIL" keyword in the $GBASIS command line of the input file. In addition, to make GAMESS(US) use this external file, one must copy the "rungms" file and modify it accordingly. The following is a list of instructions with commands that will work from a terminal. One could also use WinSCP to do all of this with a GUI rather than a TUI.
Modifiying rungms to Use Custom Basis Set File
1. Copy "rungms" from /scinet/gpc/Applications/gamess to one's own /scratch/$USER/ directory:
cp /scinet/gpc/Applications/gamess/rungms /scratch/$USER/
2. Change to the scratch directory and check to see if "rungms" has copied successfully.
cd /scratch/$USER ls
3. Edit line 147 of the vi.
vi rungms
Move the cursor down to line 147 using the arrow keys. It should say "setenv EXTBAS /dev/null". Using the arrow keys, move the cursor to the first "/" and then hit "i" to insert text. Put the path to your external basis file here. For example, /scratch/$USER/basisset. Then hit "escape". To save the changes and exit vi, type ":" and you should see a colon appear at the bottom of the window. Type "wq" (which should appear at the bottom of the window next to the colon) and then hit enter. Now you are done with vi.
Creating a Custom Basis Set File
1. To create a custom basis set file, you need create a new text document. Our group's common practice is to comment out the first line of this file by inserting an exclamation mark (!) followed by noting the specific basis sets and ECPs that are going to be used for each of the atoms. Let us the molecule Mo(CO)6, Molybdenum hexacarbonyl, as an example. Below is the first line of the the external file, which we will call "CUSTOMMO" (NOTE: you can use any name for the external file that suits you, as long as it has no spaces and is 8 characters or less).
! 6-31G on C and O and LANL2D2 ECP on Mo
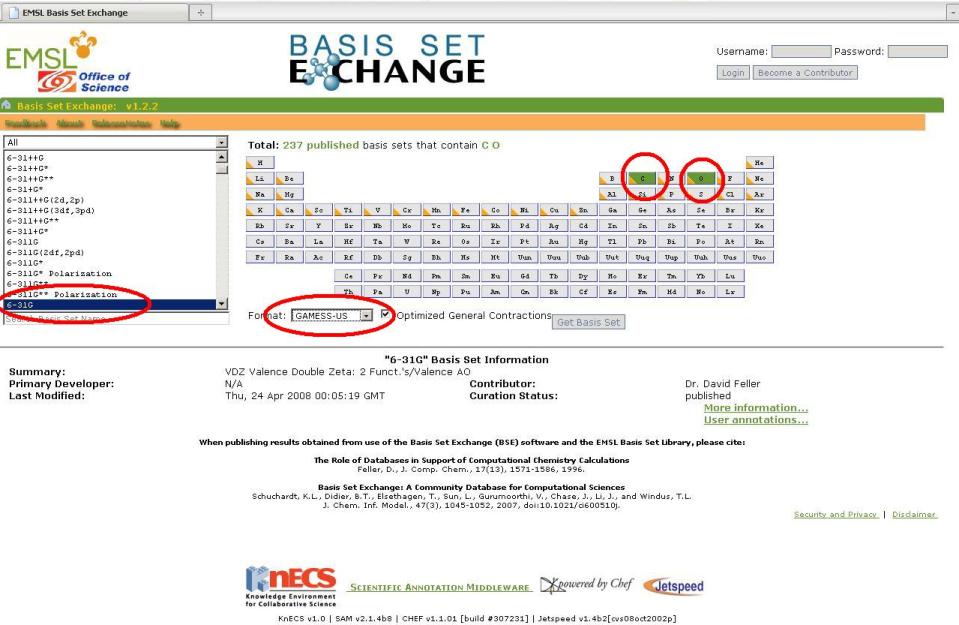
2. The next step is to visit the EMSL Basis Set exchange and select C and O from the periodic table. Then, on the left of the page, select "6-31G" as the basis set. Finally, make sure the output is in GAMESS(US) format using the drop-down menu and then click "get basis set".
3. A new window should appear with text in it. For our example case, the text looks like this:
! 6-31G EMSL Basis Set Exchange Library 10/13/09 11:12 AM ! Elements References ! -------- ---------- ! H - He: W.J. Hehre, R. Ditchfield and J.A. Pople, J. Chem. Phys. 56, ! Li - Ne: 2257 (1972). Note: Li and B come from J.D. Dill and J.A. ! Pople, J. Chem. Phys. 62, 2921 (1975). ! Na - Ar: M.M. Francl, W.J. Petro, W.J. Hehre, J.S. Binkley, M.S. Gordon, ! D.J. DeFrees and J.A. Pople, J. Chem. Phys. 77, 3654 (1982) ! K - Zn: V. Rassolov, J.A. Pople, M. Ratner and T.L. Windus, J. Chem. Phys. ! 109, 1223 (1998) ! Note: He and Ne are unpublished basis sets taken from the Gaussian ! program ! $DATA
CARBON S 6 1 3047.5249000 0.0018347 2 457.3695100 0.0140373 3 103.9486900 0.0688426 4 29.2101550 0.2321844 5 9.2866630 0.4679413 6 3.1639270 0.3623120 L 3 1 7.8682724 -0.1193324 0.0689991 2 1.8812885 -0.1608542 0.3164240 3 0.5442493 1.1434564 0.7443083 L 1 1 0.1687144 1.0000000 1.0000000
OXYGEN S 6 1 5484.6717000 0.0018311 2 825.2349500 0.0139501 3 188.0469600 0.0684451 4 52.9645000 0.2327143 5 16.8975700 0.4701930 6 5.7996353 0.3585209 L 3 1 15.5396160 -0.1107775 0.0708743 2 3.5999336 -0.1480263 0.3397528 3 1.0137618 1.1307670 0.7271586 L 1 1 0.2700058 1.0000000 1.0000000 $END
3. Now, copy and paste the text between the $DATA and $END headings onto our external text file, CUSTOMMO. We also need to change the change the name of each element to it symbol in the periodic table. Finally, we need to add the name of the external file next to the element symbol, separated by one space. Note that there should be a blank line separating the basis set information and the first, commented-out line (The line starting with the '!'). The CUSTOMMO should look like this:
! 6-31G on C and O and LANL2D2 ECP on Mo
C CUSTOMMO S 6 1 3047.5249000 0.0018347 2 457.3695100 0.0140373 3 103.9486900 0.0688426 4 29.2101550 0.2321844 5 9.2866630 0.4679413 6 3.1639270 0.3623120 L 3 1 7.8682724 -0.1193324 0.0689991 2 1.8812885 -0.1608542 0.3164240 3 0.5442493 1.1434564 0.7443083 L 1 1 0.1687144 1.0000000 1.0000000
O CUSTOMMO S 6 1 5484.6717000 0.0018311 2 825.2349500 0.0139501 3 188.0469600 0.0684451 4 52.9645000 0.2327143 5 16.8975700 0.4701930 6 5.7996353 0.3585209 L 3 1 15.5396160 -0.1107775 0.0708743 2 3.5999336 -0.1480263 0.3397528 3 1.0137618 1.1307670 0.7271586 L 1 1 0.2700058 1.0000000 1.0000000
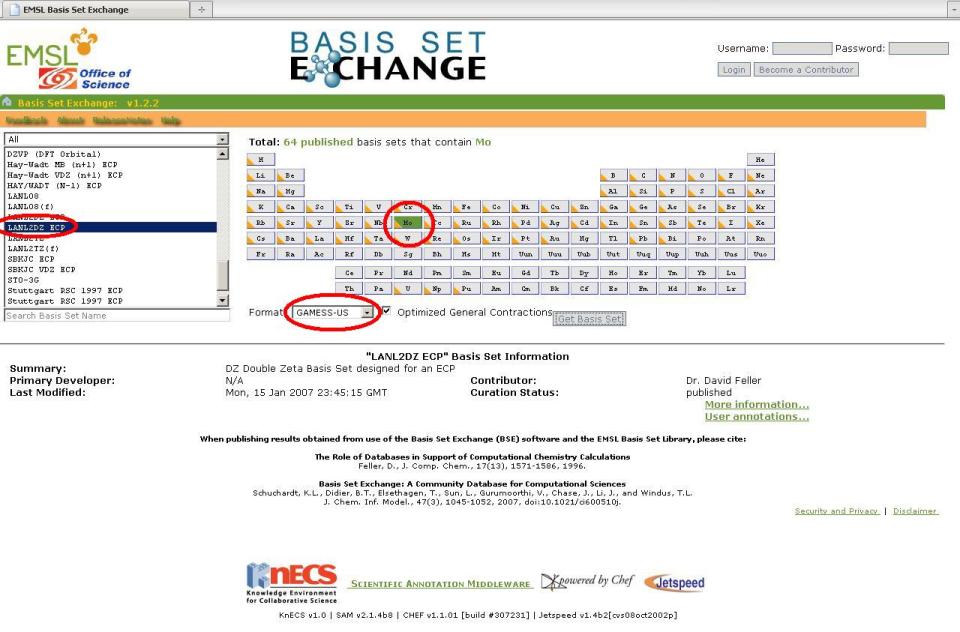
4. Repeat Step 3 above but choose Mo and select the LANL2DZ ECP instead. A new window will pop up with the basis set information as well as the ECP data we need, since we specified the LANL2DZ ECP. The ECP data is not inserted into the external file, rather it is placed into the input file itself (More on this later).
5. After copying the molybdenum basis set information, your fiished external basis set file should look like this:
! 6-31G on C and O and LANL2D2 ECP on Mo
C CUSTOMMO S 6 1 3047.5249000 0.0018347 2 457.3695100 0.0140373 3 103.9486900 0.0688426 4 29.2101550 0.2321844 5 9.2866630 0.4679413 6 3.1639270 0.3623120 L 3 1 7.8682724 -0.1193324 0.0689991 2 1.8812885 -0.1608542 0.3164240 3 0.5442493 1.1434564 0.7443083 L 1 1 0.1687144 1.0000000 1.0000000
O CUSTOMMO S 6 1 5484.6717000 0.0018311 2 825.2349500 0.0139501 3 188.0469600 0.0684451 4 52.9645000 0.2327143 5 16.8975700 0.4701930 6 5.7996353 0.3585209 L 3 1 15.5396160 -0.1107775 0.0708743 2 3.5999336 -0.1480263 0.3397528 3 1.0137618 1.1307670 0.7271586 L 1 1 0.2700058 1.0000000 1.0000000
Mo CUSTOMO S 3 1 2.3610000 -0.9121760 2 1.3090000 1.1477453 3 0.4500000 0.6097109 S 4 1 2.3610000 0.8139259 2 1.3090000 -1.1360084 3 0.4500000 -1.1611592 4 0.1681000 1.0064786 S 1 1 0.0423000 1.0000000 P 3 1 4.8950000 -0.0908258 2 1.0440000 0.7042899 3 0.3877000 0.3973179 P 2 1 0.4995000 -0.1081945 2 0.0780000 1.0368093 P 1 1 0.0247000 1.0000000 D 3 1 2.9930000 0.0527063 2 1.0630000 0.5003907 3 0.3721000 0.5794024 D 1 1 0.1178000 1.0000000
-- mzd 13 October 2009
A Modified BASH Script for Runnning GAMESS(US)
Below please find the bash script that we use to run GAMESS(US) on a single node with 8 processors.
One quirk of GAMESS(US) is that it will NOT write over old or failed jobs that have the same name as the input file you are submitting. For example: my input file name is "mo_opt.inp" and I submit this job to the queue. However, it comes back seconds later with an error. The log file says that I have typed an incorrect keyword, and lo and behold, I have a comma where it shouldn't be. Such typos can be common. If you simply try to re-submit, GAMESS(US) will fail again, because it has written a .log file and some other files to the /scratch/user/gamess-scratch/ directory. These files must all be deleted before you re-submit your fixed input file.
This script takes care of this annoying problem by deleting failed jobs with the same file name for you.
Here it is:
#!/bin/bash
#PBS -l nodes=1:ppn=8,walltime=48:00:00,os=centos53computeA
## To submit type: qsub x.sh
# If not an interactive job (i.e. -I), then cd into the directory where
# I typed qsub.
if [ "$PBS_ENVIRONMENT" != "PBS_INTERACTIVE" ]; then
if [ -n "$PBS_O_WORKDIR" ]; then
cd $PBS_O_WORKDIR
fi
fi
# the input file is typically named something like "gamesjob.inp"
# so the script will be run like "$SCINET_RUNGMS gamessjob 00 8 8"
find /scratch/user/gamess-scratch -type f -name ${NAME:-safety_net}\* -exec /bin/rm {} \;
# load the gamess module if not in .bashrc already
# actually, it MUST be in .bashrc
# module load gamess
# run the program
/scratch/user/rungms $NAME 00 8 8 >& $NAME.log
A Script to Add the $VIB Group for Hessian Restarts in GAMESS(US)
Sometimes, a optimization + vibrational analysis or just a plain vibrational analysis must be restarted. This can be because the two day time limit has been exceeded or perhaps there was an error during calculation. In any case, when this happens, the job must be restarted. In GAMESS(US), you can restart a vibrational analysis from a previous one and it will utilize the frequencies that were already computed in the failed run.
For example, if one submits the input file "job_name.inp" and it fails before it has finished, then one must utilize the file "job_name.rst", which contains data that is required to restart the calculation. This file is located in the /scratch/user/gamess-scratch directory. Data from the "job_name.rst" file must be appended at the end of the new input file (after the coordinates and ECP section if it is present) to restart the calculation, letus call it "job_name_restart.inp"
A shortened version of the "job_name.rst" file looks like this:
ENERGY/GRADIENT/DIPOLE RESTART DATA FOR RUNTYP=HESSIAN
job_name
$VIB
IVIB= 0 IATOM= 0 ICOORD= 0 E= -3717.1435124522
-5.165258381E-04 1.584665821E-02-1.206270555E-02-2.241461728E-03 3.176050715E-03
-5.706738823E-04 2.502034151E-03 5.130112290E-04-2.716945939E-03 1.357008279E-03
-1.059915305E-03 1.693526456E-03-2.957638907E-04-5.994938737E-04 9.684054361E-04
.
.
.
.
The text eventually ends with one blank line. The $VIB heading and all of the text after $VIB must be appended to the end of file "job_name_restart.inp" and then " $END" must be inserted at the very end of the file.
One could do this, one could cut cut and paste in a text editor, but we have written a small script that will do this automatically. We call it ".vib.sh" but you can call it whatever you like. Here it is:
#!/bin/bash
# script to add vibrational data for a hessian restart
awk '/\$VIB/{p=1}p;END{print " $END"}' /scratch/user/gamess-scratch/$NAME1.rst >> $NAME2.inp
To use it, simply copy it into a new text file with the extension ".sh" and make it executable. Also, you will need to edit the location of the "/scratch/user/gamess-scratch/ directory to match your user name. The two variables in the script, NAME1 and NAME2, represent the name of your ".rst" file and your new ".inp" file. In the example above, NAME1=job_name and NAME2=job_name_restart.
To run it on a gpc node without submitting it to the job queue, type:
NAME1=job_name NAME2=job_name_restart ./vib.sh
To run it in the queue, type:
qsub vib.sh -v NAME1=job_name,NAME2=job_name_restart
-special thanks to Ramses for help with this
Vienna Ab-initio Simulation Package (VASP)
Please refer to the VASP page.
User supplied content below.
Tips from the Polanyi Lab
Using VASP on SciNet
Logon using SSH login.scinet.utoronto.ca
then ssh to the TCS cluster ssh tcs01
change directory to cd /scratch/imcnab/test/Si111 - or whatever other directory is convenient.
VASP is contained in the directory imcnab/bin
To submit a job, first edit (at least) the POSCAR file and other VASP input files as necessary.
Input Files
The minimum set of input files is:
vasp.script - script file telling TCS to run a VASP job - must be edited to run in current working directory.
POSCAR - specifies supercell geometry and "ionic" positions (i.e. atomic centres) and whether relaxation allowed. Ionic positions may be given in cartesion coordinates (x,y,z in A) or "absolute", which are fractions of the unit cell vectors. CONTCAR is always in absolute coords, so after the first run of any job, you'll find yourself running in absolute coords. VMD can be used to change these back to cartesian coordinates.
INCAR - specifies parameters to run the job. INCAR is free format - can put input commands in ANY order.
POTCAR - specifies the potentials to use for each atomic type. Must be in the same order as the atoms are first met in POSCAR
KPOINTS - specifies the number and position of K-points to use in the calculation.
Any change of name or directory needs to be edited into the job script. The job script name is "vasp.script".
VASP attempts to read initial wavefunctions from WAVECAR, so if a job is run in steps, leaving the WAVECAR file on the working directory is an efficient way to start the next stage of the calculation
VASP also writes CONTCAR which is of the same format as POSCAR, and can simply be renamed if it is to be used as the starting point for a new job.
Submit the job to load-leveller with the command llsubmit ./vasp.script from the correct working directory.
can check the status of a job with llq
can cancel a job using llcancel tcs-fXXnYY.$PID where tcs number etc is shown by llq
== INPUT FILES ==
The minimum set of input files is:
vasp.script - script file telling TCS to run a VASP job - must be edited to run in current working directory.
POSCAR - specifies supercell geometry and "ionic" positions (i.e. atomic centres) and whether relaxation allowed. Ionic positions may be given in cartesion coordinates (x,y,z in A) or "absolute", which are fractions of the unit cell vectors. CONTCAR is always in absolute coords, so after the first run of any job, you'll find yourself running in absolute coords. VMD can be used to change these back to cartesian coordinates.
INCAR - specifies parameters to run the job. INCAR is free format - can put input commands in ANY order.
POTCAR - specifies the potentials to use for each atomic type. Must be in the same order as the atoms are first met in POSCAR
KPOINTS - specifies the number and position of K-points to use in the calculation.
Any change of name or directory needs to be edited into the job script. The job script name is "vasp.script".
VASP attempts to read initial wavefunctions from WAVECAR, so if a job is run in steps, leaving the WAVECAR file on the working directory is an efficient way to start the next stage of the calculation
VASP also writes CONTCAR which is of the same format as POSCAR, and can simply be renamed if it is to be used as the starting point for a new job.
Submit the job to load-leveller with the command
llsubmit ./vasp.script from the correct working directory.
can check the status of a job with llq
can cancel a job using llcancel tcs-fXXnYY.$PID where tcs number etc is shown by llq
GENERAL NOTES
MUCH faster to use ISPIN=1, no-spin (corresponds to RHF, rather than ISPIN=2 which corresponds to URHF). So far, I've not found a system where the atom positions differ, or where the calculated electronic energy differs by more than 1E-4, which is the convergence criteria set.
MUCH faster to use real space LREAL = A, NSIM=4.
So, always optimize in real space first, then re-optimize in reciprocal space. This does NOT guarantee, a one-step optimization in reciprocal space. May still need to progressively relax a large system.
Relaxing a large system. If you attempt to relax a large system in one step, it will usually fail.
The starting geometry is usually an unrelaxed molecule above an unrelaxed surface. The bottom plane of the surface will NEVER be relaxed, because this corresponds to the fixed boundary condition of REALITY.
First, relax the molecule alone (assuming you have already found a good starting position from single point calcultions, place the molecule closer to the surface than you think it should be (say 0.9 VdW radii away).
Then ALSO allow the top layer of the surface to relax. Then ALSO allow the second top layer of the surface to relax... etc... etc.
If this DOESN'T WORK: Then relax X,Y and Z separately in iterations. Example. For the following problem, representing layers of the crystal going DOWN from the top (Z pointing to the top of the screen)
Molecule
Layer 1
Layer 2
Layer 3
Layer 4
Layer 5 - fixed layer
Layer 6 - Valence H's, fixed layer
we can try the following relaxation schemes:
Successive relaxation, Layer by Layer:
(1)
Molecule XYZ Relax
Layer 1 XYZ fixed
Layer 2 XYZ fixed
Layer 3 XYZ fixed
Layer 4 XYZ fixed
Layer 5 - fixed layer.
Layer 6 - Valence H's, fixed layer
(2)
Molecule XYZ Relax
Layer 1 XYZ Relax
Layer 2 XYZ fixed
Layer 3 XYZ fixed
Layer 4 XYZ fixed
Layer 5 - fixed layer.
Layer 6 - Valence H's, fixed layer
(3)
Molecule XYZ Relax
Layer 1 XYZ Relax
Layer 2 XYZ Relax
Layer 3 XYZ fixed
Layer 4 XYZ fixed
Layer 5 - fixed layer.
Layer 6 - Valence H's, fixed layer
etc. etc... if this works then you're fine. However, it can happen that even by Layer 2, you're running into real problems, and the ionic relaxation NEVER converges. In which case, I have found the following scheme (and variations thereof) useful:
(1)
Molecule XYZ Relax
Layer 1 XYZ fixed
Layer 2 XYZ fixed
Layer 3 XYZ fixed
Layer 4 XYZ fixed
Layer 5 - fixed layer
Layer 6 - Valence H's, fixed layer
(2)
Molecule XYZ Relax
Layer 1 XYZ Relax
Layer 2 XYZ fixed
Layer 3 XYZ fixed
Layer 4 XYZ fixed
Layer 5 - fixed layer
Layer 6 - Valence H's, fixed layer
(3)
Molecule XYZ Relax
Layer 1 XYZ Relax
Layer 2 XYZ Relax
Layer 3 XYZ fixed
Layer 4 XYZ fixed
Layer 5 - fixed layer
Layer 6 - Valence H's, fixed layer
IF (3) DOESN'T converge THEN TRY
(2')
Molecule Z Relax, XY FIXED
Layer 1 Z Relax, XY FIXED
Layer 2 XYZ Relax
Layer 3 XYZ fixed
Layer 4 XYZ fixed
Layer 5 - fixed layer
Layer 6 - Valence H's, fixed layer
- you are allowing the top layers to move only UP or DOWN, while allowing the intermediate layer 2 to fully relax (actually, there is no way of telling VASP to move ALL atoms by the SAME deltaZ, but that appears to be the effect. Followed by
(2")
Molecule XYZ Relax
Layer 1 XYZ Relax
Layer 2 XYZ Relax
Layer 3 XYZ fixed
Layer 4 XYZ fixed
Layer 5 - fixed layer
Layer 6 - Valence H's, fixed layer
If (2") doesn't work, you need to go back to the output of (2') and vary the cycle - perhaps something like:
(2"')
Molecule XYZ Relax
Layer 1 XYZ Relax
Layer 2 XYZ fixed
Layer 3 XYZ fixed
Layer 4 XYZ fixed
Layer 5 - fixed layer
Layer 6 - Valence H's, fixed layer
then try (2") again.
Repeat as necessary. This scheme does appear to work quite well for big unit cells. It can be very difficult to relax as many layers as necessary in a big unit cell.
Experience on the One Per Corner Hole problem shows that it may be necessary to have a large number of UNRELAXED (i.e. BULK silicon) layers underneath the relaxed layers in order to get physically meaningful answers. This is because silicon is so elastic.
Problems and solutions:
If getting ZBRENT errors, try changing ALGO. Usually use ALGO = Fast, change to ALGO = Normal. With ALGO = Normal, NFREE now DOES correspond to degrees of freedom (maximum suggested setting is 20). Haven't found this terribly helpful.
Many calculations seem to fail after 20 or 30 ionic steps. I suspect a memory leak.
Sometimes the calculation appears to lose WAVECAR... this is not a disaster, just means a slight increase in start time as the first wavefunction is calculated.
If calculation does not finish nicely, can force a WAVECAR generation by doing a purely electronic calculation (these are pretty fast).
VASP is VERY slow at relaxing molecules at surfaces. This is because it doesn't know a molecule is a connected entity. It treats every atom independently.
THEREFORE, MUCH MUCH faster to try molecular positions by hand first. Do some sample calculations at a few geometries to find a good starting point.
ALSO, once you think you know where the molecule is to be placed, put it too close to the surface, and let it relax outwards... the forces close to the surface are repulsive, and much steeper, so relaxation is FASTER in this direction.
Climate Modelling
The Community Earth System Model (CESM) is a fully-coupled, global climate model that provides state-of-the-art computer simulations of the Earth's past, present, and future climate states.
Development of a comprehensive CESM that accurately represents the principal components of the climate system and their couplings requires both wide intellectual participation and computing capabilities beyond those available to most U.S. institutions. The CESM, therefore, must include an improved framework for coupling existing and future component models developed at multiple institutions, to permit rapid exploration of alternate formulations. This framework must be amenable to components of varying complexity and at varying resolutions, in accordance with a balance of scientific needs and resource demands. In particular, the CESM must accommodate an active program of simulations and evaluations, using an evolving model to address scientific issues and problems of national and international policy interest.
User guides and information on each version of the model can be found at the following links:
CCSM3: http://www.cesm.ucar.edu/models/ccsm3.0/ CCSM4: http://www.cesm.ucar.edu/models/ccsm4.0/ CESM1: http://www.cesm.ucar.edu/models/cesm1.0/
Running CCSM4
The scientifically validated CCSM4 runs are found in the list below (including a complete list of the model resolutions):
CCSM has significant flexibility to configure cases with respect to components, grids, and model settings. This version of CCSM has only be validated scientifically for the following full active configurations:
- 1.9x2.5_gx1v6 B_1850_CN
- 1.9x2.5_gx1v6 B_1850_RAMPCO2_CN
- 0.9x1.25_gx1v6 B_1850_CN
- 0.9x1.25_gx1v6 B_1850_RAMPCO2_CN
If the user is interested in running a "stand-alone" component configuration, the following model configurations have been validated scientifically and have associated diagnostic output as part of the release.
- 0.9x1.25_gx1v6 F_AMIP_1DEG
- 1.9x2.5_gx1v6 F_AMIP_2DEG
- 0.9x1.25_gx1v6 I and ICN
- T62_gx1v6 C
Please refer to the individual component release web pages above for information regarding alternative component configurations.
- pt1_pt1 (SHORTNAME: pt1)
- 0.47x0.63_0.47x0.63 (SHORTNAME: f05_f05)
- 0.47x0.63_gx1v6 (SHORTNAME: f05_g16)
- 0.47x0.63_tx0.1v2 (SHORTNAME: f05_t12)
- 0.9x1.25_0.9x1.25 (SHORTNAME: f09_f09)
- 0.9x1.25_gx1v6 (SHORTNAME: f09_g16)
- 1.9x2.5_1.9x2.5 (SHORTNAME: f19_f19)
- 1.9x2.5_gx1v6 (SHORTNAME: f19_g16)
- 4x5_4x5 (SHORTNAME: f45_f45)
- 4x5_gx3v7 (SHORTNAME: f45_g37)
- T62_gx3v7 (SHORTNAME: T62_g37)
- T62_tx0.1v2 (SHORTNAME: T62_t12)
- T62_gx1v6 (SHORTNAME: T62_g16)
- T31_T31 (SHORTNAME: T31_T31)
- T31_gx3v7 (SHORTNAME: T31_g37)
- T42_T42 (SHORTNAME: T42_T42)
- 10x15_10x15 (SHORTNAME: f10_f10)
- ne30np4_1.9x2.5_gx1v6 (SHORTNAME: ne30_f19_g16)
Initializing the Model Setup:
The initial setup of the model on TCS is simplified with the short script below
#!/bin/bash
export CCSMROOT=/project/ccsm/ccsm4_0_current
export SCRATCH=/scratch/$USER
export MACH=tcs
export COMPSET=B_1850_CN
export RES=f19_g16
export CASEROOT=~/runs/ccsm4_comp-${COMPSET}_res-${RES}
cd $CCSMROOT/scripts
./create_newcase -verbose -case $CASEROOT -mach $MACH -compset $COMPSET -res $RES
This script creates an 1850 control with all components of the model fully active and carbon nitrogen cycling in the land component, The resolution is 1.9x2.5 in the atmosphere and x1 in the ocean. The file is created in the ~/run directory:
For valid component sets see: http://www.cesm.ucar.edu/models/ccsm4.0/ccsm_doc/a2967.html For information on resolution sets see: http://www.cesm.ucar.edu/models/ccsm4.0/ccsm_doc/x42.html#ccsm_grids
Load Balancing:
For the NCAR bluefire load balancing table for a select set of simulations see http://www.cesm.ucar.edu/models/cesm1.0/timing/
cd ~/runs/ccsm4_comp-B_1850_CN_res-f19_g16
edit env_mach_pes.xml
<entry id="NTASKS_ATM" value="448" /> <entry id="NTHRDS_ATM" value="1" /> <entry id="ROOTPE_ATM" value="0" /> <entry id="NTASKS_LND" value="320" /> <entry id="NTHRDS_LND" value="1" /> <entry id="ROOTPE_LND" value="160" /> <entry id="NTASKS_ICE" value="64" /> <entry id="NTHRDS_ICE" value="1" /> <entry id="ROOTPE_ICE" value="0" /> <entry id="NTASKS_OCN" value="256" /> <entry id="NTHRDS_OCN" value="1" /> <entry id="ROOTPE_OCN" value="224" /> <entry id="NTASKS_CPL" value="224" /> <entry id="NTHRDS_CPL" value="1" /> <entry id="ROOTPE_CPL" value="0" /> <entry id="NTASKS_GLC" value="1" /> <entry id="NTHRDS_GLC" value="1" /> <entry id="ROOTPE_GLC" value="0" /> <entry id="PSTRID_ATM" value="1" /> <entry id="PSTRID_LND" value="1" /> <entry id="PSTRID_ICE" value="1" /> <entry id="PSTRID_OCN" value="1" /> <entry id="PSTRID_CPL" value="1" /> <entry id="PSTRID_GLC" value="1" />
Once this file is modified you can configure the case
./configure -case
You will notice that configure will change the file the you just edited and you can see the total processors used by the simulation (704 or 11 nodes in this case):
<entry id="TOTALPES" value="704" /> <entry id="PES_LEVEL" value="1r" /> <entry id="MAX_TASKS_PER_NODE" value="64" /> <entry id="PES_PER_NODE" value="64" /> <entry id="CCSM_PCOST" value="-3" /> <entry id="CCSM_TCOST" value="0" /> <entry id="CCSM_ESTCOST" value="-3" />
The task geometry used by loadleveler on TCS is located in the file: ccsm4_comp-B_1850_CN_res-f19_g16.tcs.run
Now compile the model with:
./ccsm4_comp-B_1850_CN_res-f19_g16.tcs.build
One of the pre-processing steps in this build sequence is to fetch inputdat sets (initial and boundary conditions) from the NCAR SVN server. You may want to do this yourself before you build on the datamover1 node if there is a large amount of initial condition data to transfer from the NCAR repository. datamover1 has a high bandwidth connection to the outside. Note: We have most of the input data on /project/ccsm already so this step will not be required for the more common configurations.
> ssh datamover1 Last login: Wed Jul 7 16:38:14 2010 from tcs-f11n06-gpfs user@gpc-logindm01:~>cd ~/runs/ccsm4_comp-B_1850_CN_res-f19_g16 user@gpc-logindm01:~/runs/ccsm4_comp-B_1850_CN_res-f19_g16> user@gpc-logindm01:~/runs/ccsm4_comp-B_1850_CN_res-f19_g16>./check_input_data -inputdata /project/ccsm/inputdata -export Input Data List Files Found: ./Buildconf/cam.input_data_list ./Buildconf/clm.input_data_list ./Buildconf/cice.input_data_list ./Buildconf/pop2.input_data_list ./Buildconf/cpl.input_data_list export https://svn-ccsm-inputdata.cgd.ucar.edu/trunk/inputdata/atm/cam/chem/trop_mozart_aero/aero/aero_1.9x2.5_L26_1850clim_c091112.nc /project/ccsm/inputdata/atm/cam/chem/trop_mozart_aero/aero/aero_1.9x2.5_L26_1850clim_c091112.nc ..... success
Setting the Simulation Length:
The amount of time that you would like to run the model can be set by editing env_run.xml at anytime in the setup sequence
<entry id="RESUBMIT" value="10" /> <entry id="STOP_OPTION" value="nmonths" /> <entry id="STOP_N" value="12" />
These settings will tell the model to checkpoint after each model year (12 months) and run for a total of 10 years (10 checkpoints)
Running CCSM4 on the Distributed System (TCS):
The model is now ready to be submitted to the TCS batch queue
llsubmit ccsm4_comp-B_1850_CN_res-f19_g16.tcs.run
Once the model has run through a checkpoint timing information on the simulation will be found in:
~/runs/ccsm4_comp-B_1850_CN_res-f19_g16/timing
Standard output from the model can be followed during runtime by going to:
/scratch/guido/ccsm4_comp-B_1850_CN_res-f19_g16/run
and running
tail -f <component_log_file>
The model will archive the NetCDF output in:
/scratch/$USER/archive
Cloning Simulations
A useful command that allow for the setup of multiple runs quickly is the clone command. It allows for the cloning of a case quickly (so there is no need to run the setup script above every time)
cd ~/runs /project/ccsm/ccsm4_0_current/scripts/create_clone -clone ccsm4_comp-B_1850_CN_res-f09_g16 -case ccsm4_comp-B_1850_CN_res-f09_g16_clone -v
To change the load balancing (env_mach_pes.xml) in a current simulation setup or other parameters you can do a clean build to make sure the model is rebuilt properly:
./configure -cleanmach ./ccsm4_comp-B_1850_CN_res-f19_g16.tcs.clean_build ./configure -case ./ccsm4_comp-B_1850_CN_res-f19_g16.tcs.build
Running CCSM4 on GPC
The setup script is almost identical:
#!/bin/bash
export CCSMROOT=/project/ccsm/ccsm4_0_current
export SCRATCH=/scratch/guido
export MACH=gpc
export COMPSET=B_1850_CN
export RES=f09_g16
export CASEROOT=~/runs/ccsm4gpc_comp-${COMPSET}_res-${RES}
cd $CCSMROOT/scripts
./create_newcase -verbose -case $CASEROOT -mach $MACH -compset $COMPSET -res $RES
To load balance and run the model follow the steps above: The env_mach_pes.xml configuration files needs to be modified as follows:
<entry id="MAX_TASKS_PER_NODE" value="8" /> <entry id="PES_PER_NODE" value="8" />
Use qsub to submit the model to the GPC cluster:
qsub ccsm4gpc_comp-B_1850_CN_res-f19_g16.tcs.run
Medicine/Bio
High Energy Physics
Structural Biology
Molecular simulation of proteins, lipids, carbohydrates, and other biologically relevant molecules.
Molecular Dynamics (MD) simulation
GROMACS
Please refer to the GROMACS page
AMBER
Please refer to the AMBER page
NAMD
NAMD is one of the better scaling MD packages out there. With sufficiently large systems, it is able to scale to hundreds or thousands of cores on Scinet. Below are details for compiling and running NAMD on Scinet.
More information regarding performance and different compile options coming soon...
Compiling NAMD for GPC
Ensure the proper compiler/mpi modules are loaded. <source lang="sh"> module load intel module load openmpi/1.3.3-intel-v11.0-ofed </source>
Compile Charm++ and NAMD <source lang="sh">
- Unpack source files and get required support libraries
tar -xzf NAMD_2.7b1_Source.tar.gz cd NAMD_2.7b1_Source tar -xf charm-6.1.tar wget http://www.ks.uiuc.edu/Research/namd/libraries/fftw-linux-x86_64.tar.gz wget http://www.ks.uiuc.edu/Research/namd/libraries/tcl-linux-x86_64.tar.gz tar -xzf fftw-linux-x86_64.tar.gz; mv linux-x86_64 fftw tar -xzf tcl-linux-x86_64.tar.gz; mv linux-x86_64 tcl
- Compile Charm++
cd charm-6.1 ./build charm++ mpi-linux-x86_64 icc --basedir /scinet/gpc/mpi/openmpi/1.3.3-intel-v11.0-ofed/ --no-shared -O -DCMK_OPTIMIZE=1 cd ..
- Compile NAMD.
- Edit arch/Linux-x86_64-icc.arch and add "-lmpi" to the end of the CXXOPTS and COPTS line.
- Make a builds directory if you want different versions of NAMD compiled at the same time.
mkdir builds ./config builds/Linux-x86_64-icc --charm-arch mpi-linux-x86_64-icc cd builds/Linux-x86_64-icc/ make -j4 namd2 # Adjust value of j as desired to specify number of simultaneous make targets. </source> --Cmadill 16:18, 27 August 2009 (UTC)
Running Fortran
On the development nodes, there is an old gcc. The associated libraries are not on the compute nodes. Ensure the line:
module load gcc
is in your .bashrc file.
LAMMPS
LAMMPS is a parallel MD code that can be found here.
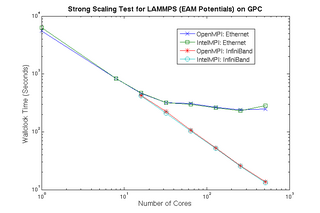
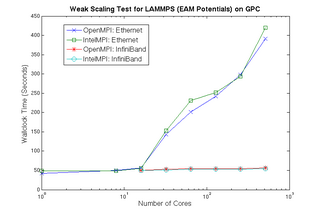
Scaling Tests on GPC
Results from strong scaling tests for LAMMPS using EAM potentials on GPC are shown in the graph on the right. Test simulation ran 500 timesteps for 4,000,000 atoms.
Results from weak scaling tests for LAMMPS using EAM potentials on GPC are shown in the graph on the right. Test simulation ran 500 timesteps for 32,000 atoms per processor.
OpenMPI version used: openmpi/1.4.1-intel-v11.0-ofed
IntelMPI version used: intelmpi/impi-4.0.0.013
LAMMPS version used: 15 Jan 2010
Summary of Scaling Tests
Results show good scaling for both OpenMPI and IntelMPI on Ethernet up to 16 processors, after which performance begins to suffer. On Infiniband, excellent scaling is maintained to 512 processors.
IntelMPI shows slightly better performance compared to OpenMPI when running with Infiniband.
--jchu 14:08 Feb 2, 2010